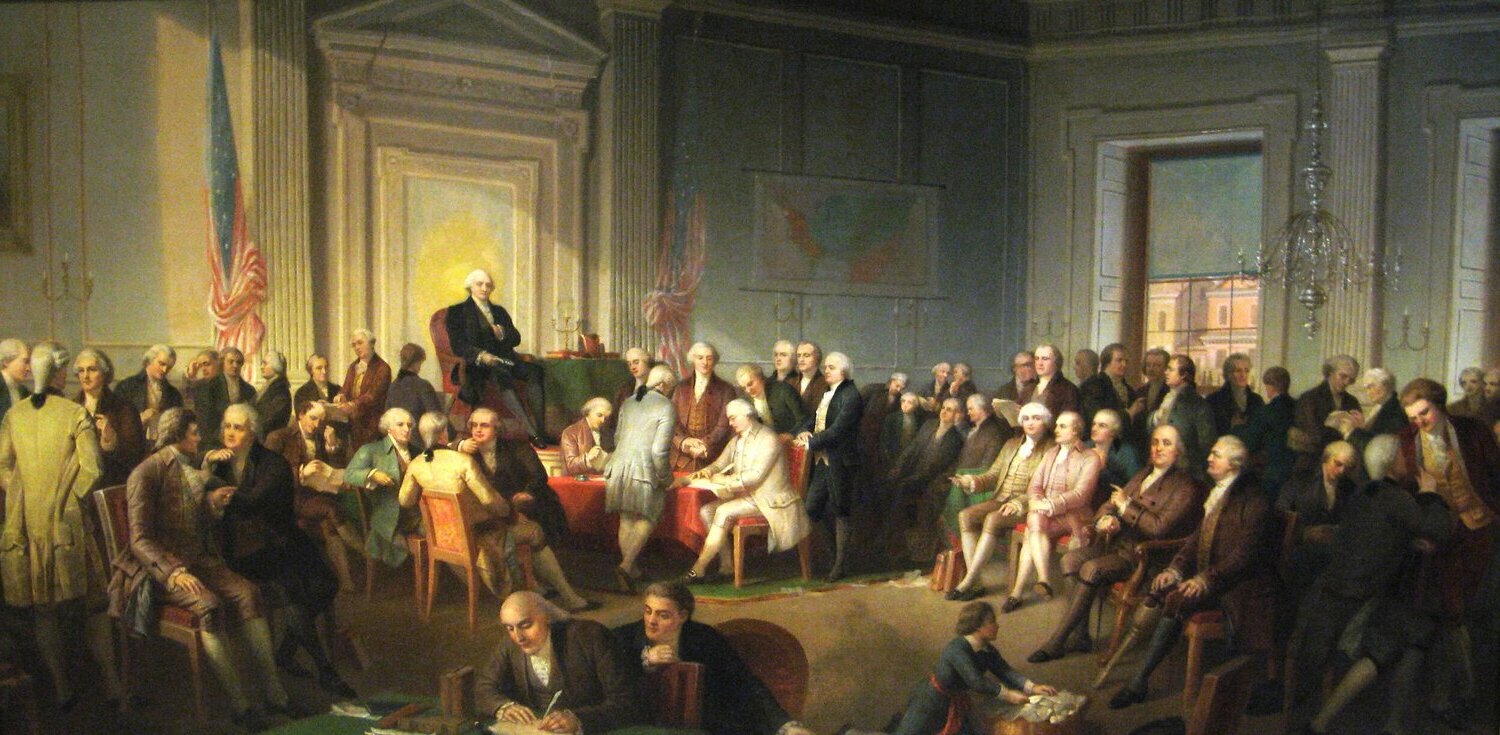
What was the Constitutional Convention? The Constitutional Convention of 1787 was a pivotal event in American history where delegates from twelve of the thirteen states gathered in Philadelphia to draft the United States Constitution. This meeting aimed to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first governing document. The convention lasted from May to September, with notable figures like George Washington, James Madison, and Benjamin Franklin playing crucial roles. Why is it significant? The resulting Constitution established the framework for the federal government and has been the supreme law of the United States ever since. This gathering not only shaped the nation's political structure but also laid the foundation for American democracy.
The Constitutional Convention: A Historic Gathering
The Constitutional Convention of 1787 was a pivotal moment in American history. Delegates from various states gathered to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and create a new framework for the government. Here are some fascinating facts about this historic event.
-
The Constitutional Convention took place in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, at the Pennsylvania State House, now known as Independence Hall.
-
The convention lasted from May 25 to September 17, 1787, spanning nearly four months of intense debate and discussion.
-
George Washington presided over the convention, lending his considerable prestige and leadership to the proceedings.
-
Fifty-five delegates attended the convention, representing 12 of the 13 states. Rhode Island was the only state that did not send delegates.
-
The delegates were a diverse group, including lawyers, merchants, farmers, and soldiers. Many had served in the Continental Congress or fought in the Revolutionary War.
Key Figures and Their Contributions
Several prominent figures played crucial roles in shaping the Constitution. Their ideas and compromises helped create the document that governs the United States today.
-
James Madison, often called the "Father of the Constitution," played a significant role in drafting the document and advocating for a strong central government.
-
Benjamin Franklin, the oldest delegate at 81, provided wisdom and a calming influence during heated debates.
-
Alexander Hamilton, a strong proponent of a powerful federal government, contributed to the Federalist Papers, which argued for the Constitution's ratification.
-
Gouverneur Morris is credited with writing the preamble to the Constitution, which begins with the famous words, "We the People."
-
Roger Sherman proposed the Great Compromise, which led to the creation of a bicameral legislature with the House of Representatives and the Senate.
The Great Compromise and Other Key Agreements
The delegates faced numerous challenges and disagreements. Through negotiation and compromise, they managed to create a balanced and effective framework for the new government.
-
The Great Compromise resolved the issue of representation by establishing a two-house Congress, with proportional representation in the House and equal representation in the Senate.
-
The Three-Fifths Compromise determined that each enslaved person would be counted as three-fifths of a person for purposes of taxation and representation.
-
The Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise allowed the federal government to regulate interstate and international commerce but prohibited any laws banning the slave trade for 20 years.
-
The Electoral College was established as a compromise between electing the president by popular vote and election by Congress.
-
The delegates agreed on a system of checks and balances to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
The Ratification Process
After the convention, the proposed Constitution had to be ratified by the states. This process involved intense debate and required the approval of nine out of the thirteen states.
-
The Federalist Papers, written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, were a series of essays advocating for the Constitution's ratification.
-
Delaware was the first state to ratify the Constitution on December 7, 1787.
-
New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify the Constitution on June 21, 1788, making it the law of the land.
-
Rhode Island was the last state to ratify the Constitution on May 29, 1790.
-
The Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments to the Constitution, was added in 1791 to address concerns about individual liberties and limit the power of the federal government.
Legacy of the Constitutional Convention
The Constitutional Convention left a lasting legacy, shaping the United States' government and influencing democracies worldwide.
-
The Constitution established a federal system of government, dividing powers between the national government and the states.
-
The principles of separation of powers and checks and balances have become fundamental aspects of the American political system.
-
The Constitution has been amended 27 times, allowing it to adapt to changing circumstances and continue to serve as the foundation of American democracy.
Final Thoughts on the Constitutional Convention
The Constitutional Convention of 1787 was a pivotal moment in American history. It brought together some of the brightest minds of the time, including George Washington, James Madison, and Benjamin Franklin. They debated, compromised, and ultimately crafted a document that has stood the test of time. The U.S. Constitution established the framework for a new government, balancing power between the states and the federal system. It also introduced the system of checks and balances, ensuring no single branch would dominate. The Bill of Rights, added shortly after, guaranteed essential freedoms and rights. Understanding the Constitutional Convention helps us appreciate the foresight and dedication of the Founding Fathers. Their work laid the foundation for the democratic principles we cherish today. The legacy of the Convention continues to influence and guide the United States, proving its enduring significance.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


