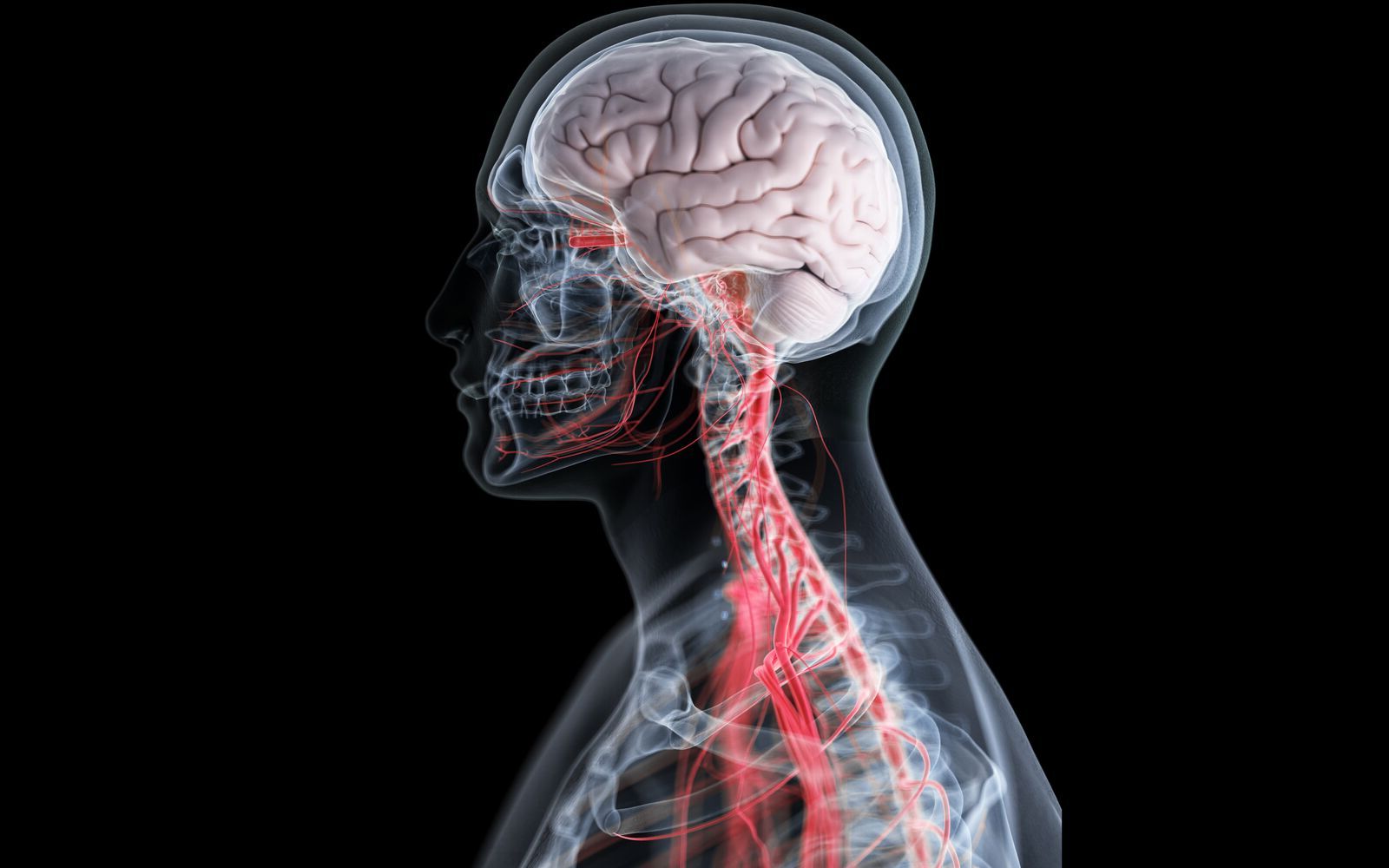
Ever wondered how your brain, this squishy mass inside your skull, manages everything from your heartbeat to your deepest thoughts? Yes, the human brain is a marvel of nature, packed with mysteries and astonishing facts that might just blow your mind. In this engaging read, we're diving into 20 fascinating facts about the human brain that will make you appreciate this incredible organ even more. From its unbelievable processing power to its ability to dream and create, prepare to be amazed by what's happening inside your head. So, buckle up for a thrilling ride through the twists and turns of your own brain. You're in for some real surprises!
Key Takeaways:
- The human brain, despite its size, is a powerful energy hog, using 20% of the body's energy. It's a complex network that can learn and adapt, and it's protected by the skull and the blood-brain barrier.
- Sleep is crucial for brain health, as it helps remove toxins. The brain's ability to heal and adapt, along with the impact of diet and genetics, are fascinating areas for future research.
Understanding the Human Brain
The human brain, a marvel of nature, serves as the command center for the human nervous system. It receives signals from the body's sensory organs and outputs information to the muscles. This complex organ, despite its soft consistency, holds the key to our thoughts, memory, emotions, speech, and movement.
Size Matters
- Despite popular belief, the size of the human brain does not directly correlate with intelligence. An average adult brain weighs about 3 pounds and contains roughly 86 billion neurons.
The Powerhouse of Energy
- Your brain is an energy hog. It uses about 20% of your body's total energy, even though it only makes up about 2% of your body weight. This energy is crucial for maintaining healthy brain functions, including thought processing and neurotransmission.
A Network Like No Other
- Neurons in the brain communicate through intricate networks. Each neuron can form thousands of connections to other neurons, creating a complex web of communication pathways.
Memory and Learning
-
Human memory is a dynamic and plastic system. It's not stored in just one part of the brain but is distributed throughout. The hippocampus, for instance, plays a significant role in the formation of new memories.
-
Learning and memory are facilitated by the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This ability is known as neuroplasticity.
The Brain's Protective Measures
-
The brain is well-protected by the skull and three layers of tissue called meninges. Additionally, cerebrospinal fluid cushions the brain, providing further protection against injury.
-
The blood-brain barrier is a selective barrier that prevents many substances from entering the brain from the bloodstream, protecting it from potential harm.
Sleep and the Brain
- Sleep plays a critical role in brain health. During sleep, the brain removes toxins that accumulate during waking hours, which is vital for maintaining cognitive functions.
The Emotional Center
- The amygdala, a small almond-shaped structure, is crucial for emotional processing. It plays a key role in the experience of emotions such as fear and pleasure.
Language and the Brain
- Language processing involves multiple areas of the brain. The Broca's area is involved in speech production, while the Wernicke's area is key for understanding language.
The Aging Brain
- As we age, the brain undergoes natural changes. Brain mass shrinks, and the speed of neurotransmission can slow down. However, mental exercise and a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate these effects.
The Brain's Healing Ability
- The brain has a limited capacity to heal after injury. Neuroplasticity can aid in recovery, allowing other parts of the brain to take over functions lost due to damage.
The Unconscious Brain
- A significant portion of our brain's activity occurs without our conscious awareness. This includes processes like breathing, heartbeat, and digestion, which are regulated by the autonomic nervous system.
Creativity and the Brain
- Creativity involves multiple brain regions. The frontal lobes, for instance, are associated with divergent thinking, which is the ability to come up with multiple solutions to a problem.
The Brain and Exercise
- Regular physical exercise not only benefits the body but also has a positive impact on brain health. It can improve cognitive function, reduce the risk of dementia, and enhance mood and sleep.
The Myth of Multitasking
- The brain is not truly capable of multitasking. What we perceive as multitasking is actually the brain switching tasks rapidly, which can reduce productivity and increase errors.
The Brain's Adaptability
- The human brain is incredibly adaptable. It can learn new skills and adapt to changes in the environment, thanks to its plasticity.
The Influence of Diet on Brain Health
- A healthy diet can have a significant impact on brain health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can support brain function and protect against cognitive decline.
The Role of Genetics
- Genetics play a crucial role in the development and function of the brain. However, environmental factors and lifestyle choices also significantly influence brain health.
The Future of Brain Research
- Advances in technology and medicine continue to unravel the mysteries of the human brain. Future research promises to offer new insights into brain diseases, cognitive enhancement, and the potential for brain-computer interfaces.
A Final Nod to Our Brain's Marvels
We've journeyed through a fascinating exploration of the human brain, uncovering its complexities and capabilities. From its unparalleled processing power to its ability to adapt and learn, our brains are truly remarkable. We've seen how emotions and memory intertwine, how sleep plays a crucial role in brain health, and even how our brains keep evolving throughout our lives. These insights not only deepen our understanding but also inspire awe for the organ that makes us who we are. Remember, nurturing our brains with good nutrition, exercise, and mental challenges is key to unlocking their full potential. Let's not take for granted this incredible organ that orchestrates our thoughts, memories, and emotions. Here's to celebrating and caring for our brains, the most intricate and powerful part of our being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


