Ever wondered what makes you, well, you? What's the secret sauce in those cells that crafts your unique being? DNA is the answer, folks! This twisty, turny molecule is like the blueprint of life, holding all the juicy details about what makes each creature on this planet unique. From eye color to that weird little toe you got from your grandma, DNA's got the 411. But how much do we really know about this microscopic marvel? Buckle up, because we're about to unravel 20 mind-blowing facts about DNA that'll make your jaw drop. Ready to get your mind twisted in the best way possible? Let's dive into the helix and uncover the mysteries of what's really zipping around inside our cells.
Key Takeaways:
- DNA is the blueprint for all living things, with 99.9% similarity among humans. It determines traits, helps solve crimes, and holds potential for personalized medicine and even extraterrestrial life.
- Mutations in DNA can lead to genetic disorders or drive evolution, while advancements in DNA technology are revolutionizing medicine and opening up exciting possibilities for the future.
What is DNA?
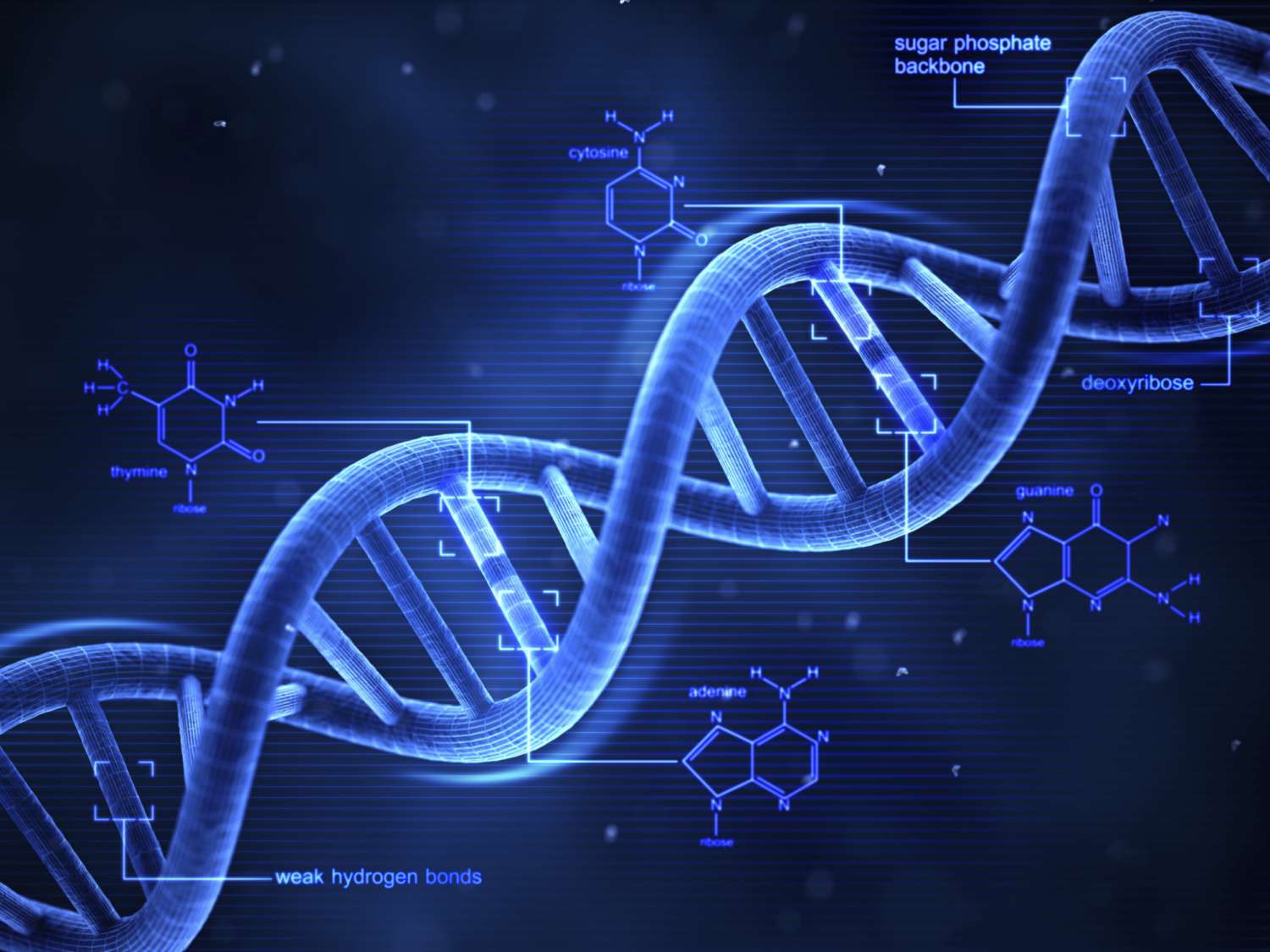
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, serves as the blueprint for all living organisms. It contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive, and reproduce. By encoding genetic information, DNA molecules dictate how cells operate and ensure that this precious data is passed from one generation to the next.
-
Every human cell contains approximately 3 billion base pairs of DNA. These pairs are organized into chromosomes, which reside in the cell nucleus.
-
Human DNA is about 99.9% identical in every person. It's the 0.1% variation that contributes to the differences in appearance, health, and more among individuals.
How Does DNA Work?
Understanding how DNA functions can be fascinating. It's not just a static library of information but a dynamic set of instructions that cells use to perform their tasks.
-
DNA works by encoding information into genes, which are segments of DNA that determine specific traits or functions. These genes are then transcribed into RNA and finally translated into proteins, the workhorses of the cell.
-
Interestingly, less than 2% of human DNA codes for proteins. The rest, often called "junk DNA," has functions that are still not fully understood, including regulating gene activity and maintaining chromosome structure.
DNA and Heredity
One of the most well-known roles of DNA is in heredity, where genetic information is passed down from parents to offspring.
-
Children inherit half of their DNA from each parent, which is why they share traits with both. This genetic mix is what makes each person unique.
-
Identical twins are an exception, as they share 100% of their DNA, having developed from the same fertilized egg that split into two.
DNA Mutations and Their Impact
Not all DNA sequences stay the same, and changes in these sequences can have significant effects.
-
Mutations in DNA can lead to genetic disorders or increase the risk of developing diseases like cancer. These mutations can be inherited or acquired due to environmental factors.
-
On the flip side, mutations are also a driving force behind evolution, introducing genetic diversity that can lead to new traits beneficial for survival.
The Role of DNA in Forensics
DNA analysis has become a powerful tool in forensic science, helping to solve crimes and identify individuals.
-
Since every person's DNA is unique (except for identical twins), it can be used to match crime scene evidence to potential suspects or identify victims.
-
Forensic scientists can now obtain DNA profiles from just a few cells, making it possible to solve cases that are decades old.
DNA Beyond Earth
The search for extraterrestrial life often includes looking for DNA or DNA-like molecules, highlighting its importance in the definition of life.
-
Scientists speculate that if extraterrestrial life exists, it might also use some form of genetic material to pass on information, though it may not necessarily be DNA.
-
The discovery of DNA or a similar molecule on other planets would be groundbreaking, providing clues about the universality of life's genetic code.
DNA in Medicine and Health
Advancements in DNA technology have had a profound impact on medicine, leading to personalized treatments and better disease understanding.
-
Genetic testing can identify mutations that increase the risk of developing certain diseases, allowing for early intervention or tailored treatment plans.
-
Gene therapy, a technique that involves altering the genes within a person's cells, is a growing area of research aimed at curing genetic diseases by fixing defective DNA.
The Future of DNA Research
As our understanding of DNA continues to evolve, so too do the possibilities for its application in various fields.
-
Scientists are working on using DNA for data storage, capitalizing on its ability to compactly store vast amounts of information for thousands of years.
-
Another exciting frontier is synthetic biology, where researchers create new life forms or redesign existing ones by writing new DNA code, potentially revolutionizing medicine, energy, and environmental management.
-
The CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology, often described as "molecular scissors," allows for precise alterations to DNA. This innovation holds promise for correcting genetic defects and treating diseases at their genetic roots.
-
With ongoing research, we're also getting closer to understanding the mysteries of "junk DNA," which could unlock new insights into human evolution and disease.
-
The International Barcode of Life project aims to catalog every species on Earth using a short DNA sequence, which could transform our understanding of biodiversity and aid in conservation efforts.
-
Lastly, the study of ancient DNA, extracted from fossils, is shedding light on the evolution and migration patterns of extinct species, including our own ancestors, providing a fascinating glimpse into the past.
A Final Peek into DNA's Mysteries
We've journeyed through the twists and turns of DNA, uncovering facts that dazzle and educate. From its role as life's blueprint to its potential in solving historical mysteries, DNA continues to amaze. Its impact stretches from medical breakthroughs to answering age-old questions about human ancestry. As we've seen, DNA isn't just a scientific marvel; it's a bridge connecting past, present, and future, offering insights that were once thought impossible. Whether it's through the lens of forensic science, genetic engineering, or tracing evolutionary history, DNA holds keys to unlocking mysteries of life itself. So, next time you hear about DNA in the news or in a conversation, remember the incredible journey you've taken through its helical structure and the endless possibilities it represents. Here's to the endless exploration of life's fundamental building block!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


