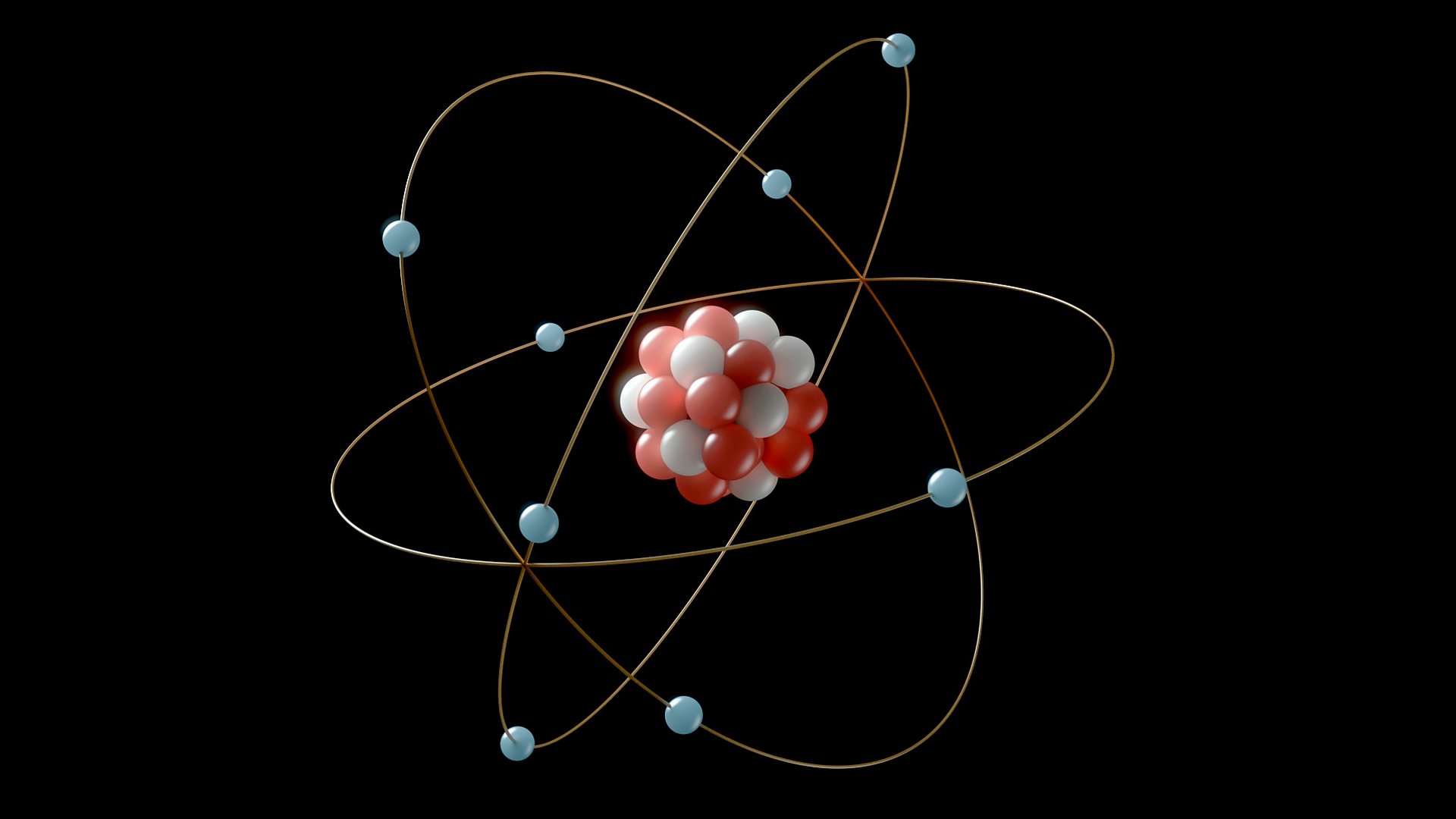
Atoms are the building blocks of everything around us. But what exactly are they? Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain the properties of an element. Imagine them as tiny Lego pieces that come together to form everything from your favorite book to the stars in the sky. Each atom consists of a nucleus, made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons. These particles interact in fascinating ways, creating the diverse world we live in. Understanding atoms can help us grasp the basics of chemistry, physics, and even biology. Ready to dive into some mind-blowing facts about these tiny powerhouses? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Atoms are the tiny building blocks of everything around us, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. They consist of even smaller particles and play a crucial role in our daily lives.
- The study of atoms has led to groundbreaking discoveries and theories, shaping our understanding of the universe. Atoms are not just confined to Earth; they are the building blocks of the entire universe, making us literally made of stardust.
What Are Atoms?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. Everything around us, from the air we breathe to the food we eat, is made up of atoms. Here are some fascinating facts about these tiny particles.
- Atoms are incredibly small, measuring about 0.1 to 0.5 nanometers in diameter.
- The word "atom" comes from the Greek word "atomos," meaning indivisible.
- Atoms consist of three main particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around it.
- The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines its element.
Atomic Structure
Understanding the structure of atoms helps us grasp how they interact and form the world around us.
- The nucleus of an atom is extremely dense and contains most of the atom's mass.
- Electrons are much smaller than protons and neutrons, with a mass nearly 1/1836 that of a proton.
- Neutrons have no electric charge, while protons are positively charged, and electrons are negatively charged.
- The arrangement of electrons in an atom's electron cloud determines its chemical properties.
- Atoms can gain or lose electrons, becoming ions with positive or negative charges.
Elements and Isotopes
Elements are pure substances made of only one type of atom. Isotopes are variations of elements with different numbers of neutrons.
- There are 118 known elements, each with a unique number of protons.
- Hydrogen is the simplest element, with just one proton and one electron.
- Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, differing in the number of neutrons.
- Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive and decay over time.
- Radioactive isotopes have applications in medicine, such as in cancer treatment.
Atomic Bonds
Atoms bond together to form molecules and compounds, creating the diverse materials we see around us.
- Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons.
- Ionic bonds occur when atoms transfer electrons, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other.
- Metallic bonds involve a "sea" of shared electrons among metal atoms.
- Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions between molecules, important in water's unique properties.
- The strength and type of atomic bonds determine a material's properties, like hardness and melting point.
Atomic Theory and Discoveries
The study of atoms has evolved over centuries, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and theories.
- Democritus, an ancient Greek philosopher, first proposed the idea of atoms around 400 BCE.
- John Dalton developed the first modern atomic theory in the early 19th century.
- J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in 1897 using a cathode ray tube.
- Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 revealed the existence of the atomic nucleus.
- Niels Bohr proposed a model of the atom with electrons in specific energy levels.
Quantum Mechanics and Atoms
Quantum mechanics provides a deeper understanding of atomic behavior, especially at very small scales.
- Electrons exhibit both particle and wave-like properties, known as wave-particle duality.
- The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that we cannot precisely know both the position and momentum of an electron.
- Quantum mechanics describes electrons in terms of probability clouds rather than fixed orbits.
- The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers.
- Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where particles become interconnected, affecting each other instantaneously over distances.
Atoms in Everyday Life
Atoms play a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives, from technology to biology.
- Silicon atoms are essential in making computer chips and electronic devices.
- Carbon atoms form the backbone of organic molecules, including DNA and proteins.
- Atoms in metals like iron and aluminum are used in construction and manufacturing.
- The oxygen we breathe is made of two oxygen atoms bonded together (O2).
- Atoms in food provide the nutrients and energy our bodies need to function.
Fun and Surprising Facts
Atoms hold many surprises and interesting tidbits that can spark curiosity and wonder.
- There are more atoms in a single glass of water than there are glasses of water in all the oceans on Earth.
- If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be the size of a pea.
- The human body contains approximately 7 octillion atoms (that's 7 followed by 27 zeros).
- Atoms are mostly empty space; if you removed all the empty space from the atoms in your body, you would be the size of a grain of salt.
- The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number and properties.
Atoms in the Universe
Atoms are not just confined to Earth; they are the building blocks of the entire universe.
- Hydrogen and helium are the most abundant elements in the universe, formed shortly after the Big Bang.
- Stars, including our Sun, generate energy by fusing hydrogen atoms into helium.
- Heavier elements like carbon, oxygen, and iron are formed in the cores of stars through nuclear fusion.
- Supernovae, the explosive deaths of massive stars, scatter these heavier elements into space, seeding new stars and planets.
- The atoms in your body were once part of ancient stars, making you literally made of stardust.
The Fascinating World of Atoms
Atoms are the building blocks of everything around us. From the air we breathe to the stars in the sky, atoms make up all matter. Understanding them helps us grasp the basics of chemistry, physics, and even biology. They consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons, each playing a crucial role in the atom's structure and behavior.
Atoms are incredibly small, yet they hold immense power. Nuclear reactions, which involve changes in an atom's nucleus, can release vast amounts of energy. This energy powers the sun and can be harnessed for electricity in nuclear power plants.
Learning about atoms opens up a world of knowledge. It helps us appreciate the complexity and beauty of the universe. So next time you look at anything, remember, it's all made up of tiny, fascinating atoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


